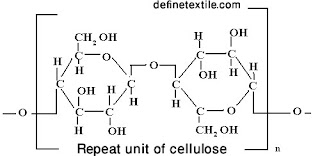
The types of winding are given below.
According to density the winding are two types. These are,
1. Precision winding.
2. Non precision winding.
According to type of package the winding are five types. These are,
1. Cone winding package.
2. Pirn winding package.
3. Flange winding package.
4. Cheese winding package.
5. Cop winding package.
According to the build of the package the winding are three types. These are,
1. Parallel winding package.
2. Near parallel winding package.
3. Cross parallel winding package.
According to methods of drive the winding are two types. These are,
1. Positive or direct drive.
2. Negative or direct drive
According to the future of automation the winding are two types. These are,
1. Conventional winding.
2. Modern winding.